

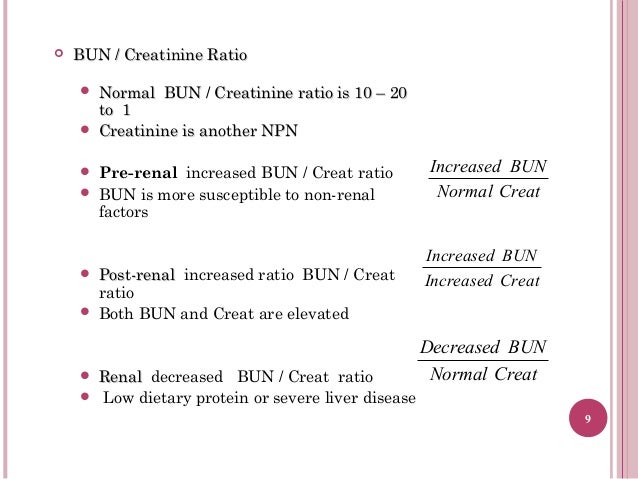
If the rate of rise exceeds 3 mg/dL per day, skeletal muscle or increased catabolism is also present. If the rate of rise is less, residual renal function exists. In acute renal failure, serum creatinine will rise 1 to 2 mg/dL per day. Causes of high creatinine levels include intrinsic renal disease, urinary tract obstruction, and reduced renal blood flow from congestive heart failure, shock or dehydration.

Serum creatinine is increased when GFR is decreased. For these reasons, AKI may be under recognized in patients with sepsis. Serum creatinine increases relatively slowly after AKI because creatinine distributes in a large volume and an increase is often masked in patients receiving large volume of fluids and positive fluid balance. Low urine output of <0.5 mL/kg/h for more than 6 hours is also characteristic of AKI. Current international consensus criteria for AKI include a relative increase in serum creatinine of 50% or more from baseline within 7 days or an absolute increase of 0.3 mg/dL or more within a 48 hour interval. Creatinine levels are reduced during pregnancy because of increased GFR.Īcute kidney injury (AKI) is a sudden loss of renal function occurring over several hours to days. Elderly patients have decreased muscle mass and decreased creatinine production. Patients with liver disease may have a normal serum creatinine even though creatinine clearance is less than 60 mL/min. Advanced liver disease causes low serum creatinine because of decreased hepatic conversion of creatine to creatinine, decreased dietary protein intake, muscle wasting, and increased renal tubular secretion of creatinine. Serum creatinine is decreased in individuals with small stature, cachexia, amputations, or muscle disease. If a previous baseline creatinine is not available for comparison, a serum creatinine level of 1.2 mg/dL might be considered clinically insignificant. A change in serum creatinine from 0.6 to1.2 mg/dL reflects a 50% decline in GFR, even though creatinine is still within the normal range. Moderate changes in GFR may not be detected by serum creatinine levels. Serum creatinine is a crude indicator of renal disease. Creatinine is removed from plasma by glomerular filtration and then excreted in the urine without significant tubular reabsorption.
The amount of creatinine formed is proportional to muscle mass. About 1 to 2% of the creatine in muscle is converted to creatinine daily (15 to 30 mg creatinine per kg body weight). The diagnostic usefulness of serum creatinine as an indicator of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is based upon its constant production from muscle creatine and its relatively constant renal excretion rate. Measurement of serum creatinine is the most widely used measure of renal function.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
